Cardiac Glycosides
Some plants containing cardiac glycosides:
Christmas rose Helleborus niger,
foxglove Digitalis
purpurea, lily of the valley (Convallaria majalis)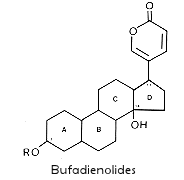 and white
water lily (Nymphaea alba).
and white
water lily (Nymphaea alba).
Cardiac glycosides are divided into two main types:
1. Bufadienolides are C24 steroids
The primary cardiac glycoside present in Helleborus is the bufadienole, hellebrin. Hellebrigenin, the aglycone of hellebrin is more potent than the glycoside itself.
2. Cardenolides are C23 steroids
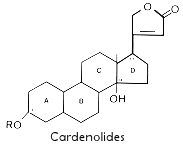
Cardenolides are the most prevalent. They have a hormonal nature as substances.
Their effects are on the heart and kidney. They have a strong, bitter and disagreeable taste.
- Cardiotonic = affect contractions of the heart muscle.
- Break down in fermentation by enzymatic action.
- Treatment: atropine and activated charcoal, lidocaine for H. viridis
- Assumed mechanism of action: inhibition of the Na+, K+-ATPase resulting in increased intracellular sodium and subsequent intracellular calcium leading to enhanced muscle contraction in cardiac tissue.
Cardenolides are classified according to the chemical composition of their aglycones as lanataglucosides A, B, C, D and E. Only Digitalis lanata, the woolly foxglove contains all five forms.e. The entire foxglove plant is toxic. Symptoms of poisoning include dizziness, vomiting, irregular heart beat, and delerium or halucinations.
Digitonin is probably the best known derivative of the Digitalis cardenolides. It is a drug derived from D. purpurea. It is used in modern medicine to increase the force of the systolic contractions and prolong duration of the diastolic phase in congestive heart failure. Digitalis drugs lower venous pressure in hypersensetive heart ailments, elevate blood pressure in a weak heart act as a diuretic, and reduce edema. However, the therapeutic dose is dangerously close to the lethal dose.